Solutions
Horse Construction offers full range of structural strengthening materials with technical supports, documentation supports, products supports, project supports.
Repair and Maintenance of Fiber Composite Materials
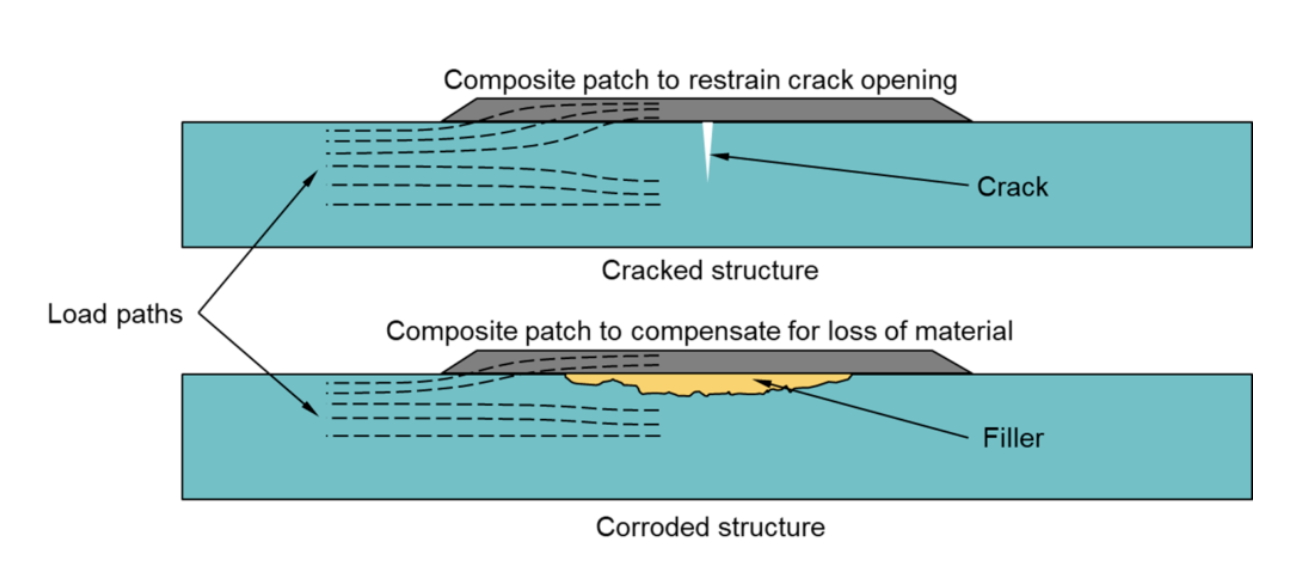
Composite repair involves applying fiber-reinforced composite laminates to the affected structure through mechanical fastening or adhesives. As shown in Figure 1, the patch transfers part of the load in the structure, thereby reducing the stress in the infrastructure. Compound repairs can be used for:
Restore or restore the strength of the structure deteriorated due to corrosion, fatigue cracks or other damage;
Strengthen the structure to increase the carrying capacity;
Strengthen the structure to reduce deflection or increase buckling capacity;
Increase the fatigue life of the structure; or
Compensation for design or construction defects.
The composite material has excellent fatigue and corrosion resistance and is very suitable for many maintenance situations. Composite materials have a very high strength-to-weight ratio, and the properties of orthotropic materials can be tailored for specific applications. Repair can be done quickly and can follow complex or irregular surfaces. No hot work is involved, so there is no risk of fire, heat-affected areas or thermal residual stresses. Compound repairs can usually be carried out without interruption of service. For example, traditional welded pipeline repairs require the pipeline to be closed during maintenance, while compound repairs can be performed while the pipeline is still running. Iconic examples of composite materials used to maintain steel and concrete structures can now be seen on the 336-meter-long Westgate Bridge over the Yarra River in Melbourne. The bridge has been structurally reinforced, using a total of more than 20 tons of carbon fiber, making it one of the largest carbon reinforcement projects in the world
To ensure long-term effectiveness, composite repairs need to be carefully designed. Although boron and aramid can be used in some professional applications, glass fiber or carbon fiber reinforced materials are most commonly used. In order to maximize repair efficiency, the fiber reinforcement direction should be aligned with the main load path. As shown in Figure 2, different repair configurations can be used. Compared with simpler repair procedures, more complex scarf repairs can reduce the shear stress of the bonding line. The repair film needs to be carefully tapered to minimize peel stress at the edges, which may limit repair strength and durability. As shown in Figure 3, the repair design is usually expressed in terms of the required thickness, the required length from the defect and the taper.
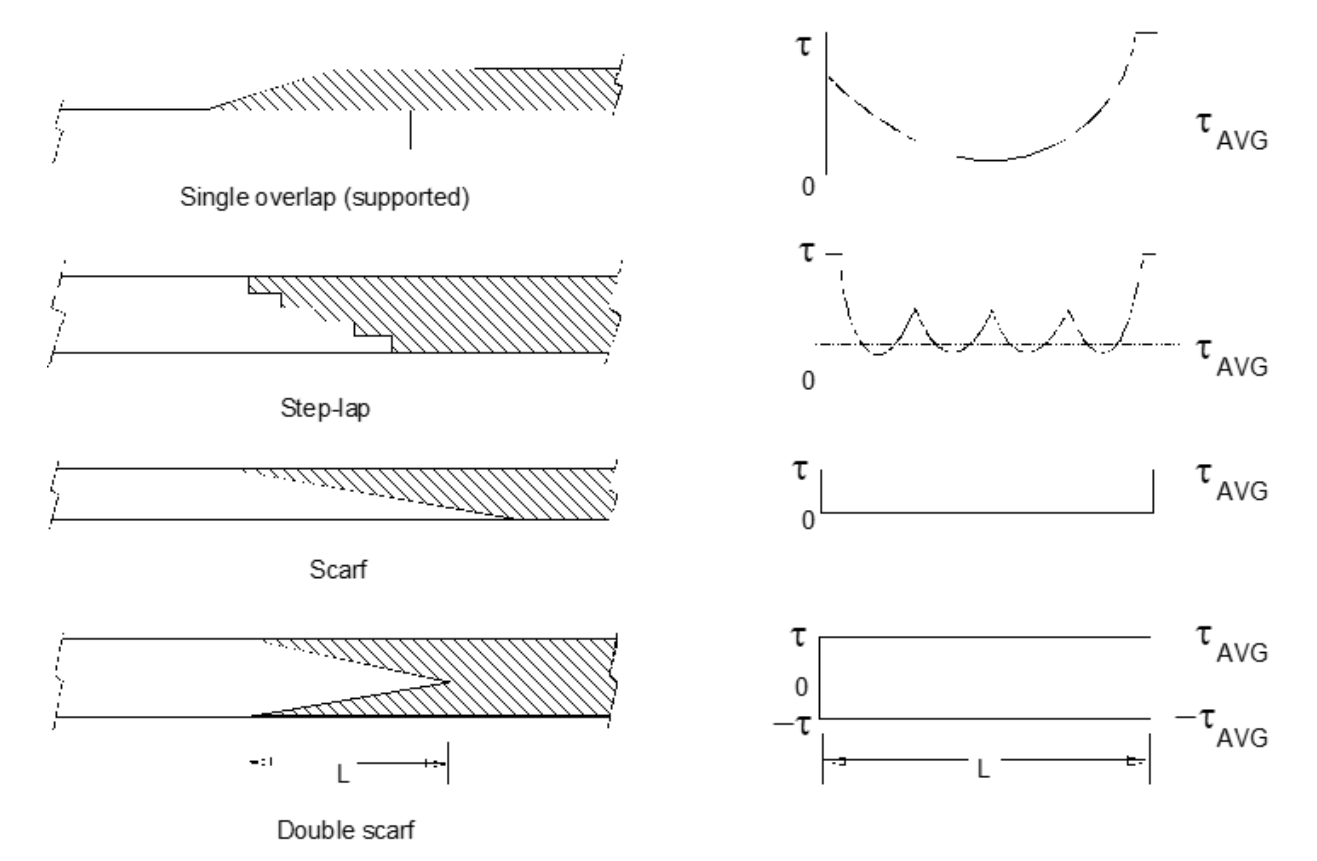
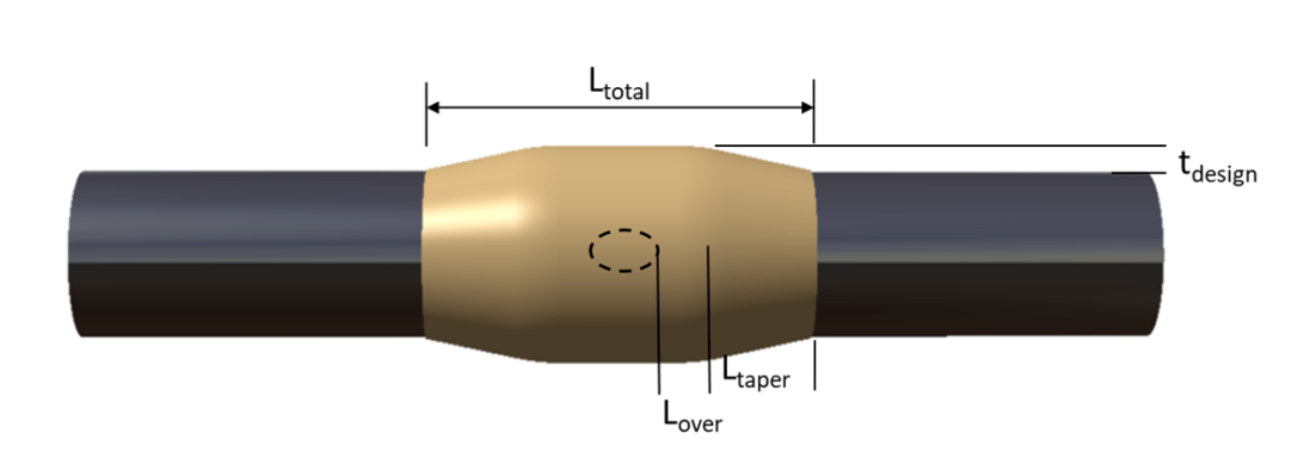
Composite materials may not always be suitable for repairs, and there are some issues that affect durability and performance, including:
Environmental factors, including exposure to chemicals, extreme temperatures or thermal cycles;
Galvanic corrosion caused by the incompatibility between the materials used in the maintenance and the basic structure;
Fire protection requirements as organic matrix materials and adhesives may burn and generate harmful gases; and
Destructive behavior, because composite materials may be sensitive to impacts and cuts.
The composite prosthesis can be directly applied to the structure by wet layup or using a prepreg system and then cured in place. Alternatively, the pre-cured laminate can be mechanically fixed or glued to the structure. The repair of bonded composite materials firstly depends on high-quality surface treatment. The surface must be clean and free of contamination in order to form a high-energy surface for the adhesive to form an effective bond. In composite structures, this step usually includes removing all damaged materials and filling if necessary, cleaning with solvents, sanding the patch area to be pasted and ensuring that the resulting surface is free of particles or other contaminants. For metals and other materials, a similar process is used, although a primer can be used to ensure good adhesion. For adhesive repair, the choice of adhesive is critical. Epoxy resins are the most commonly used and provide the highest performance.
You can find anything here you are in need of, have a trust trying on these products, you will find the big difference after that.

High strength, unidirectional carbon fiber wrap pre-saturated to form a carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP) wrap used to strengthen structural concrete elements.

High strength, unidirectional carbon fiber fabric pre-saturated to form a carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP) fabric used to strengthen structural concrete elements.

High strength, unidirectional carbon fiber sheet pre-saturated to form a carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP) sheet used to strengthen structural concrete elements.